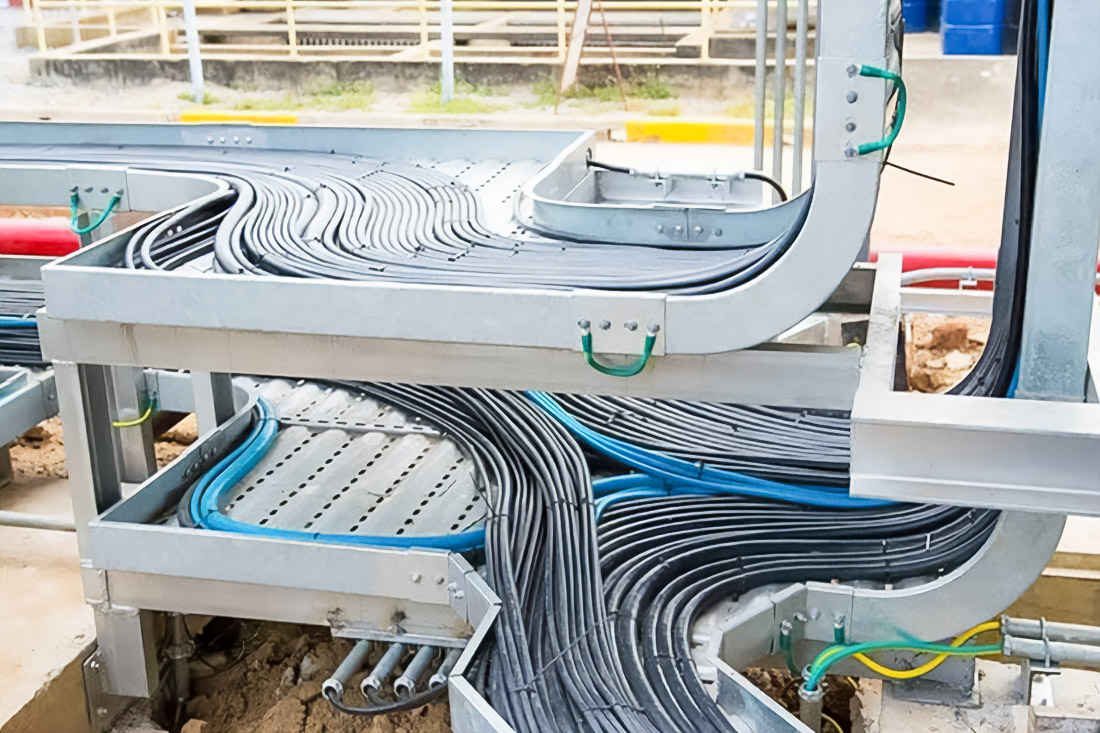
Modern electrical infrastructure of large buildings, industrial facilities and engineering structures is impossible without a well-designed cable management system. Cable trays perform a key function – they form an organised, safe and durable environment for laying power, control and low-current cables. In conditions of high temperature, humidity, dust and aggressive atmosphere, the requirements for such systems increase many times.
The Role of Cable Trays in the Safety and Reliability of Systems
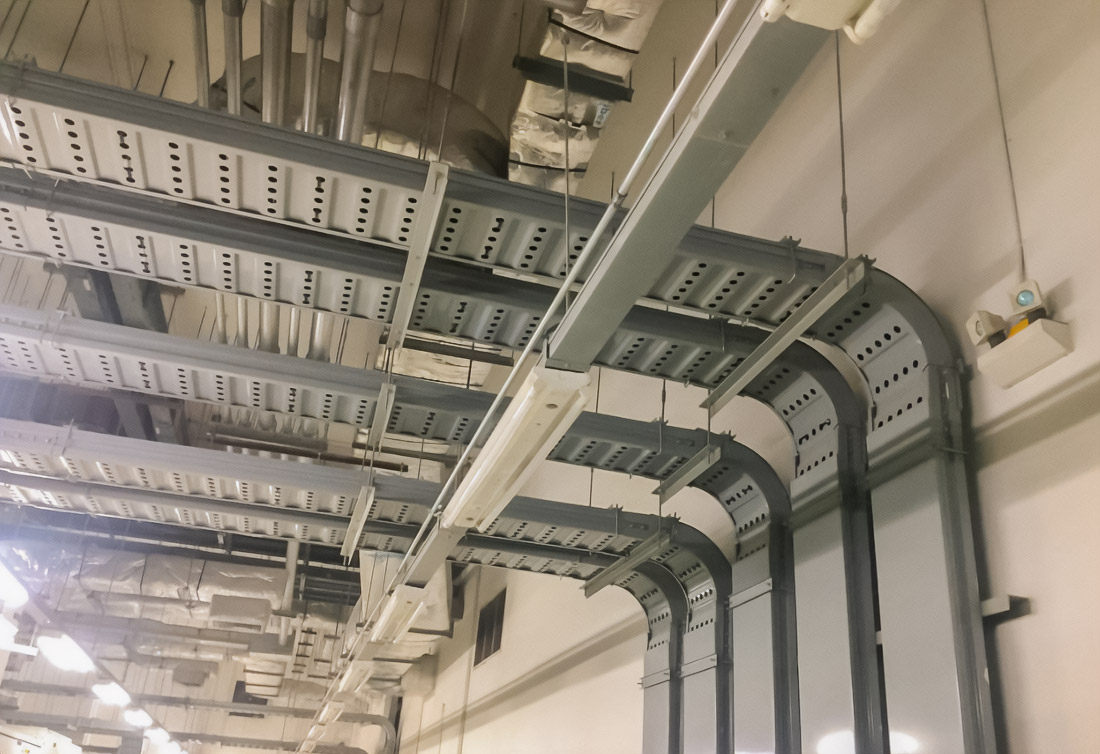

The cable tray is not just a mechanical support. It is part of a unified system that affects the operational reliability, fire safety and durability of the entire electrical network. A properly selected cable tray system reduces the risk of short circuits, overheating, and mechanical damage to cables, as well as simplifies maintenance and upgrades.
The organised laying of cables ensures:
- Stable ventilation of cables and efficient heat dissipation
- Protection against mechanical influences and contamination
- Monitoring of permissible load and load-bearing capacity
- Secure grounding and electrical continuity of the system
Climatic Factors and their Impact on Cable Systems
High ambient temperature, high humidity and the presence of dust directly affect the service life of the electrical infrastructure. Overheating of cables leads to degradation of insulation and reduction of permissible current load. That is why ventilation and control of the fill factor are of fundamental importance.
Operational practice shows that when the cable trays are filled by more than 50%, the heat sink deteriorates dramatically. The optimal range is considered to be 40-50%, which allows you to maintain the air gap for cooling and provides a margin for future expansion of the system.
Main Types of Cable Trays and Applications
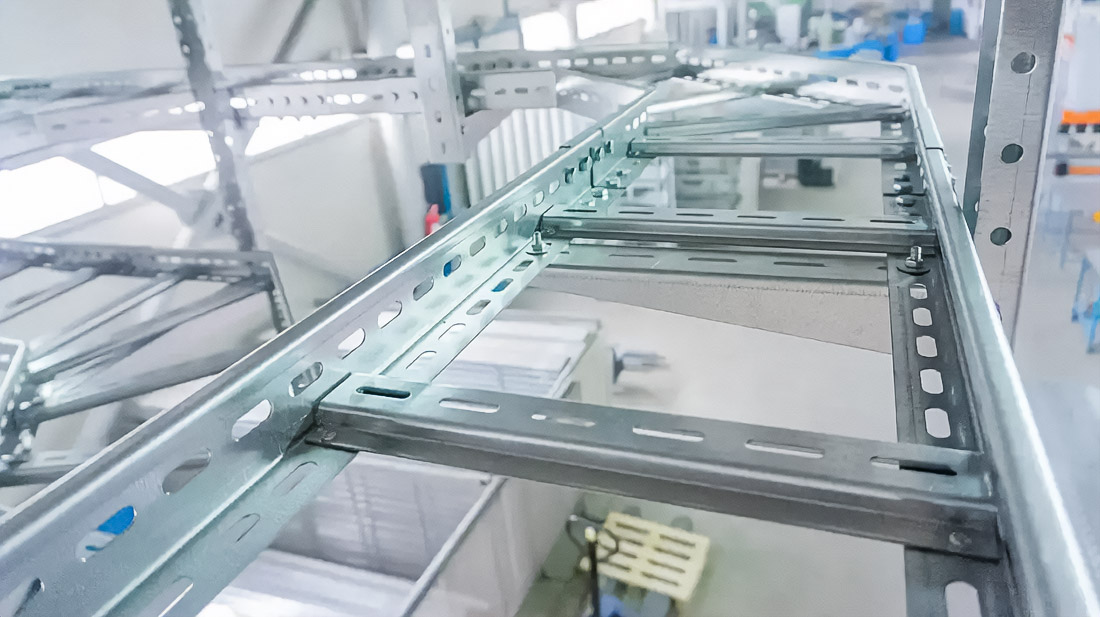

The choice of the type of cable tray is determined by the operating conditions, the type of cables, and the ventilation and protection requirements.
Ladder cable trays are used for heavy power cables and long trails. The open design ensures maximum ventilation and reduces the risk of overheating in high-temperature conditions.
Perforated trays combine mechanical support and ventilation. They are suitable for commercial buildings, infrastructure facilities and systems with a large number of small diameter cables.
Solid-bottom trays are used to protect sensitive cables from dust, moisture, and electromagnetic interference. When using them, it is especially important to take into account the thermal load and carry out calculations of the rating.
Mesh cable tray systems are widely used in data centres, server rooms and telecommunication hubs. Their lightweight design, high adaptability and excellent ventilation contribute to lower operating costs for cooling.
A wire mesh cable tray allows quick on-site cutting and shaping, making it especially effective for installations with frequent changes, high cable density and strict cooling requirements. This type of tray significantly contributes to reducing operational cooling costs.
Materials and Corrosion Resistance
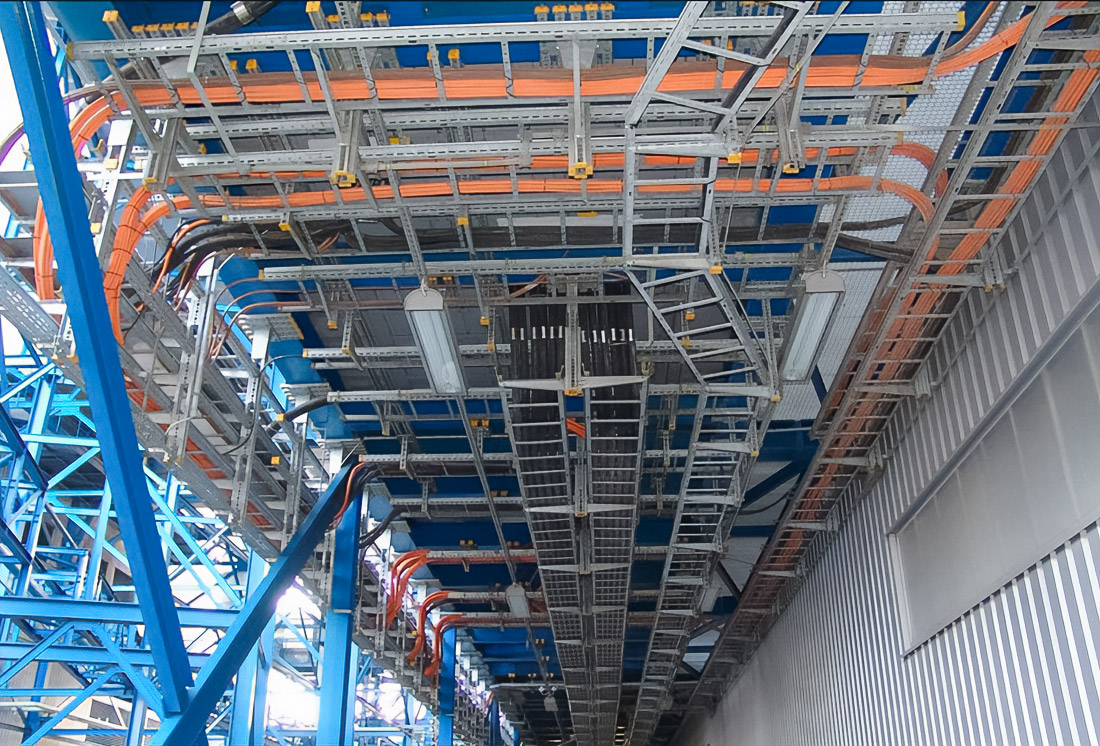

The material of the cable trays directly determines their durability. In an aggressive environment, corrosion resistance becomes a key factor.
Hot-dip galvanised steel is widely used for outdoor and industrial installations due to its protective zinc layer.
Stainless steel is used in conditions of high humidity, salt exposure and chemical activity.
Composite materials have full corrosion resistance, low weight and electrical insulation, which increases the level of electrical safety.
The service life of cable systems, with the right choice of material and correct installation, reaches 20-40 years, which makes initial engineering calculations critically important.
Loads, Supports, and Thermal Expansion
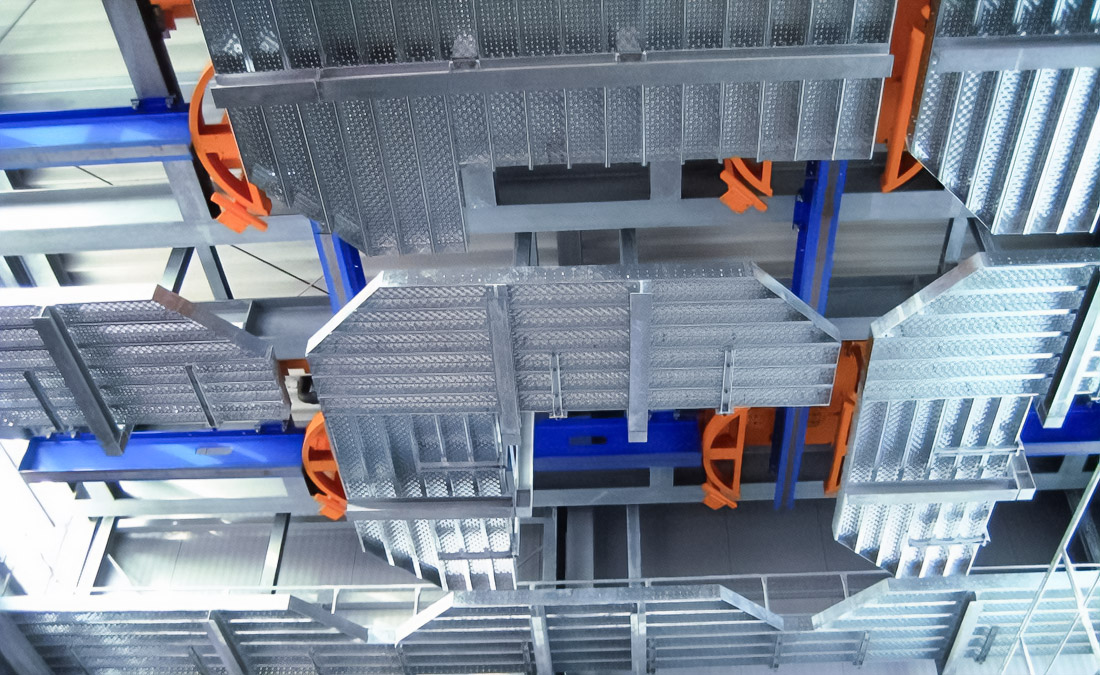
The bearing capacity of a cable tray is determined by its width, side height, metal thickness and the distance between the supports. The typical installation pitch of the supporting structures is 1.5–2 metres, but it should decrease under high loads.
Thermal expansion requires special attention. Metal systems lengthen when heated, and the absence of compensation gaps leads to deformation of the route. In practice, compensation elements are used with an interval of 25-30 metres, which prevents warping and damage to cables.
Grounding and Electrical Continuity
The safety of cable systems is impossible without reliable grounding. All elements must form a continuous electrical circuit with low resistance. The use of connecting plates, flexible jumpers and tightening control of fasteners are essential conditions for preventing dangerous potentials on metal structures.
Economy and operational advantages
The use of modular cable tray systems reduces installation time by up to 40% compared to traditional installation methods. In addition, properly selected accessories reduce the risk of accidents during operation by up to 70%, reducing repair costs and downtime.
The growth in demand for such solutions is confirmed by the steady dynamics of the market: the regional segment shows annual growth of about 7%, which is associated with the development of infrastructure, industrial facilities and data centres.
Cable trays are an integral part of modern electrical infrastructure. Their role goes far beyond cable support – it is an element of safety, reliability and long-term efficiency of the entire system. In conditions of high temperature, humidity, and aggressive environments, only an integrated approach that takes into account ventilation, load, materials, standards, and installation practices can create a truly stable and durable cable system.
Proper design and compliance with engineering requirements at the installation stage form the basis for uninterrupted operation of electrical networks for decades to come.

Basketball lover, singer, gourmet. Works in an IT company as a web designer.